The gestation period for a puppy is just 9 weeks! Witness this remarkable transformation as puppies develop inside their mother’s womb.
Inside a mother's womb!
Dog Pregnancy ~ Day by Day

Day 1
First day of mating.
The stud releases 500+ million sperm. Depending on the size of the male, he can produce up to 10 million sperm per pound of bodyweight.
The sperm are not immediately able to fertilize an egg as it must go through stages of ripening.
The female may or may not have ovulated (released eggs) at this time; which is a good reason to have progesterone levels checked so we know when the ideal breeding time is.

Day 1 continued
The sperm travels through the cervix to the fallopian tubes, which can take between 45 minutes - 3 hours.
Once here the sperm ripens, which can take 5 - 10 hours.

Day 2
The sperm look for an egg to fertilize. If the female has not ovulated yet, “normal” dog semen can live 3-to-7 days while inside the female.
The better the semen quality, the more flexibility there is in ovulation timing.

Day 3
After 48 hours it is possible to have a second mating.
Day 4
The eggs are now fertilized.
In the first trimester there is no need to change anything as she is able to continue exercise and maintain regular food rations.
However, in warmer summer months, excessive activity is discouraged as it can cause overheating in some dogs.

Days 5-11
Fertilized eggs will make their way down the fallopian tubes into the uterine horns.
During the second week of pregnancy the fertilized eggs are becoming embryos. Splitting as they form a more complex cell that will become a puppy. They will split from 2 cells, to 4 cells, and ultimately into a complex 64 cell embryo where it becomes a fetus with a head and spine. The tiny embryos will remain in the uterus for the remainder of the gestation period.
The female should still be fed and exercised normally during this time.

Days 12-13
Embryos move around in the fluid filled uterus looking for a suitable place to nest. The fluid is a food source for the embryos before nesting.
They measure around 0.5 - 0.8mm.

Day 14
As they migrate in the womb, individual embryos are diffused in uterine corners, where they will later nest into the uterine walls.
They continue to receive vital nutrients and life support from the fluid. Feed and exercise normally; however, monitor your female for increased appetite and provide for her developing needs accordingly. There should be no sudden or unnecessary changes to her diet.

Day 15
During the next two weeks, the internal organs of the embryo will develop and extra care should be taken.
She will be very sensitive to any changes in her normal routine, food, exercise, outings, etc.
Any abrupt changes can disrupt the development of the embryo which can lead to reabsorption of fetus by the female through day 39.

Days 16-18
The embryo measures just over 1mm.
On day 17 the embryos are nesting and the nervous system begins to develop, followed by the head and body.
By day 18, the placenta begins to develop.
The nipples of the female are enlarging and turning pink.
The fur on her belly and around the nipples may become thinner.
Size of embryo is now about 2 - 3mm.
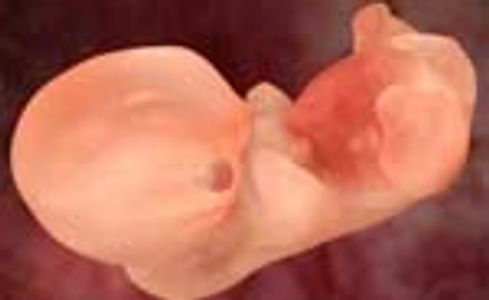
Days 19-20
Development of the internal organs begins.
Development of placenta continues.
A slight discharge may be noticeable from your female which comes from around the placenta at this stage.
Embryo size is about 4mm

Day 21
Placenta is formed and development of the heart begins.
The size is around 5 - 8mm

Day 22
The female may have morning sickness and loss of appetite, this is a result of hormonal changes and tension in the womb. Sometimes vomiting may occur and she may seem lethargic.
She may also have a clear (egg white color) vaginal discharge.
Divide food into smaller portions.

Days 23-24
The fetus starts to develop eyes, ears, nose, jaw and liver.
Due to the rapid development of all major organs, the actual fetal growth is slow. This is an ideal time for ultrasound.
Size is of embryos are around 10mm.

Days 25-27
The heartbeat can be seen during an ultrasound.
The fetus begins to develop teeth, spine and limbs.
Limit the amount of strenuous movement with the female.
Size is 14 - 20 mm, which is about the size of a walnut.

Day 28
There is ossification of the jaw and the skull of the fetus.
The shape of the fetus changes originally from ovoid shape to spherical.
Size is about 17 - 25 mm.
The fourth week of fetus development is considered to be one of the most formative stages of the pregnancy, when the growing puppies
are most vulnerable to damage and developing defects.
Limit rough play and particularly strenuous exercise in female.
-0003.jpg/:/cr=t:11.67%25,l:0%25,w:100%25,h:76.67%25/rs=w:600,h:300,cg:true)
Day 29
The fetus is already very similar to a miniature dog.
Start to gradually increase food; taking care not to overfeed.

Day 30
Complete ossification of the jaw and skull.
This image is of the uterine horn at 30 days gestation with 10 embryos.
Size of each embryo is about 2 - 3cm.

Days 31-33
Growth of sensory hairs on the chin, eyebrows, and nose.
There is growth of fingers; ossification of the nose, ribs and leg bones.
In mid-gestation each fetus reaches approximately 20% of birth size. There is still a danger of fetuses being absorbed until day 39.

Days 34-35
Completion of the development of all major organs.
Female starts to change behavior, she may be quieter and noticeably more sensitive.
Her abdomen and external genitalia begin to slightly increase.
She starts to have an increased appetite and food should be increased by 10%
Size average around 35mm.

Days 36-38
The slow growth period ends and the fetus starts to grow rapidly. It starts with developing reproductive system, and continues with skeletal ossification and scapula.
Day 37 begins the fastest growth stage of the fetus. The uterus starts to expand and you will see an increase in volume in the rib area of the female. You may also notice enlargement of the mammary glands.

Days 39-40
Growth of the fetus accelerates, skeletal ossification continues.
Almost all the internal organs are established.
First signs of hair begin to appear on the head.
Eyes are closed.
Fetus size about 65 - 70mm.

Day 41
Ossification of the spine and fingers.
The fetus is now about 30% of its total birth size.

Days 42-43
If an ultrasound is done, you can easily see leg buds and toes.
Finally, they look like little puppies!

Days 44-47
Ossification of pelvis and fetus. The puppies will start to grow fur & then pigmentation. Eyelids are about to start forming.
The females uterus now occupies 2/3 of the abdominal cavity.
It is recommended to feed 3 to 5 times a day in smaller portions while increasing the overall amount by 15-20%.
No strenuous movements or jumping is advised.

Days 48-50
The fetuses reach 75% of birth size. Organs are well developed and the belly is crowded with puppies.
We may start to see sporadic movement of the puppies.
The female is visibly larger as the fetuses push the internal organs around in the digestive tract.
The puppies will continue to grow and develop, and now look almost completely fully formed.
The female may or may not lose her appetite during this period.
We feed more often in smaller doses increased to 25% or more.

Days 51-54
The last of the internal organs begin to develop (lungs).
She will spend a lot of time resting as she prepares for birth.
For some females, spontaneous milk release can occur.
The total daily feed should be increased by 50%.

Days 55-57
The body of the fetus is covered with fur; however, the fur on the feet is less visible.
Claws are developed and calcification of teeth begins.
Pigmentation of skin starts.
Movements of fetuses are more pronounced.
Significantly swollen mammary glands.
The female is resting and preparing for birth.
Size of fetus is 145 mm.

Day 58
The puppies have developed lungs and from this stage forward the puppies are viable.
Avoid all rough play as it could lead to early labor. Ideally the puppies should spend several more days in the womb.
You should be able to feel and/or see the puppies moving in her.
Her body will start producing colostrum which is crucial for puppy survival as it provides both immunoglobulins & nutrition for the newborns. Colostrum is 5 times more concentrated than regular milk and necessary for the first 2 days post-partum.
She will likely begin nesting.
Feed as much as she will eat as she prepares for the birth!

Days 59-66
It is time to be prepared and have everything on hand as she may give birth any day now.
As her body is preparing for birth, her abdomen will become loose.
Her body temperature is recorded each morning and evening as there is a decrease in body temperature approximately 12-24 hours before birth.
She will likely refuse any food a day prior to birth.
Hormonal changes will induce uterine contractions as labor begins.
During this stage, she may be very restless and unsettled.
Delivery of puppies can be different for each female.

Birthday!
Welcome to the world little one!
Video, pictures, & content of this page are the property of National Geographics "In the Womb Series"
Copyright © 2026 Patriot Labrador Retrievers - All Rights Reserved.